Introduction
The startup ecosystems of India and the United States are among the most powerful in the world — each thriving on innovation, technology, and entrepreneurial energy. But while both produce unicorns and global success stories, they differ sharply in funding patterns, growth strategies, success rates, and risk factors.
Let’s break down how Indian and US startups compare when it comes to funding, growth, success, and risk — and what the future looks like for both.
🇮🇳 Indian Startups: Growth Fueled by Scale and Affordability
India’s startup boom began around 2014 with the launch of Startup India. Today, it’s home to 100+ unicorns across fintech, edtech, healthtech, SaaS, and logistics. Brands like Zomato, Paytm, and Byju’s are household names.
🔹 Success & Growth Drivers:
- Massive Market Size: Over 1.4 billion people offer an unmatched consumer base.
- Digital Transformation: UPI, Jio’s 4G expansion, and affordable internet made online business models thrive.
- Government Push: Startup India, Digital India, and tax incentives create a supportive ecosystem.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower operating costs help startups grow fast even with smaller funding.
- Global Expansion: Indian SaaS startups like Zoho and Freshworks have achieved international recognition.
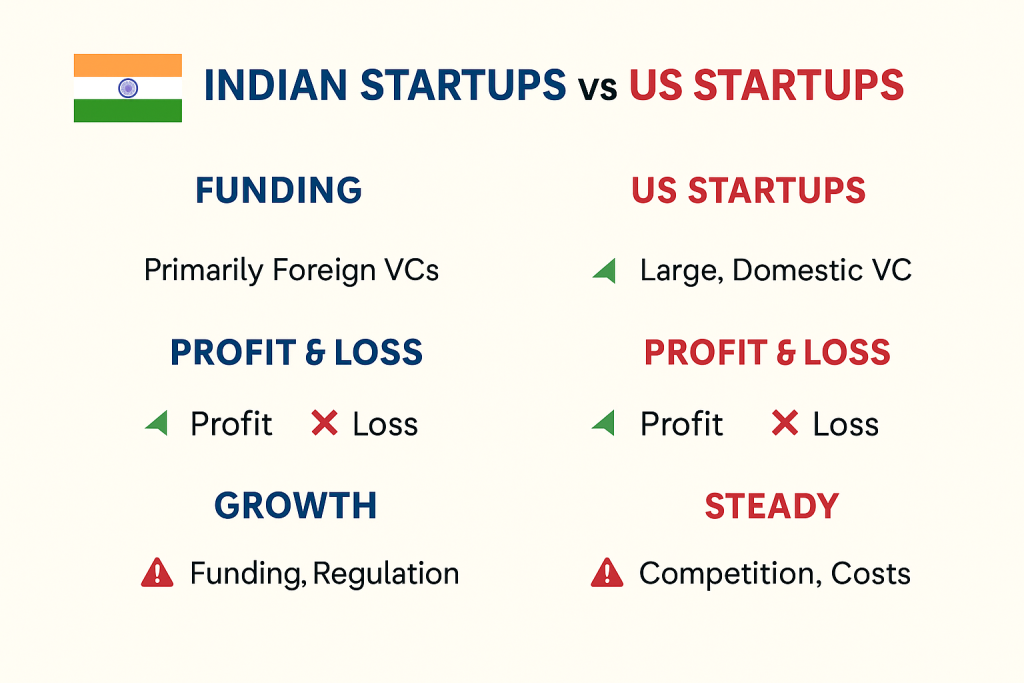
Funding Landscape: India
Investor Base: Dominated by global players like Sequoia Capital, Tiger Global, Accel, and SoftBank.
Funding Size: Average seed round ranges from $100K to $1M, Series A from $3M–$10M — smaller compared to US rounds.
Key Trend: Shift from “growth at any cost” to profitability-focused investments post-2022.
Sectors Attracting Most Funds: Fintech, e-commerce, SaaS, and EV tech.
Recent Trend: Rise in domestic funds (e.g., Blume Ventures, Bharat Innovation Fund).
Risk Factors for Indian Startups:
- Overdependence on foreign capital — global market shifts can affect local funding.
- Regulatory challenges around data, taxation, and FDI.
- High competition in B2C sectors with price wars.
- Slow exit opportunities due to limited IPOs or acquisitions.
Even so, India’s resilience and adaptability make it a rapidly growing innovation hub with global ambitions.
🇺🇸 US Startups: Innovation Backed by Deep Capital
The US remains the startup capital of the world, home to 700+ unicorns and innovation leaders like Tesla, Airbnb, Stripe, and OpenAI. Its strength lies in combining capital, talent, and technology.
🔹 Success & Growth Drivers:
- Global-first Approach: Startups design products for international markets from day one.
- Research & Development: Collaboration with top universities and labs drives deep-tech innovation.
- Risk-taking Culture: Failure is viewed as experience — fueling creativity and experimentation.
- High Revenue Models: Customers are willing to pay premium prices, enabling faster profitability.
- Support System: Accelerators (Y Combinator, Techstars), strong angel networks, and legal infrastructure
Funding Landscape: United States
- Investor Base: Thousands of VC firms, angel investors, and corporate venture funds.
- Funding Size: Average seed round $2M–$5M, Series A typically $10M–$30M.
- Accessibility: Easier to secure early-stage funding with a strong idea and traction.
- Government Support: Indirect via tax incentives, SBIR grants, and research funding.
- Top Sectors for Investment: AI, biotech, clean energy, cybersecurity, and SaaS.
Risk Factors for US Startups:
- High operational costs (especially for talent and compliance).
- Tough competition — only ~10% of startups survive beyond five years.
- Regulatory scrutiny around data, AI, and monopolistic behavior.
- Market Saturation — several niches already dominated by giants like Google and Amazon.
Despite the risks, the US continues to dominate the global innovation index with a strong pipeline of next-gen startups.
Comparison Snapshot
| Aspect | Indian Startups 🇮🇳 | US Startups 🇺🇸 |
|---|---|---|
| Market Size | Huge, cost-sensitive | Mature, premium-focused |
| Funding Range | $100K–$10M (avg) | $2M–$30M (avg) |
| Investor Type | Mostly foreign VCs | Domestic + institutional |
| Growth Strategy | Volume & affordability | Innovation & disruption |
| Success Rate | Moderate, improving | High, but competitive |
| Risk Factors | Funding, regulation, exit | Cost, competition, regulation |
| Key Sectors | Fintech, Edtech, SaaS | AI, Biotech, SaaS, SpaceTech |
| Exit Options | Limited IPO/M&A | Strong IPO & M&A ecosystem |
Success Highlights
India:
Zomato – Listed on stock exchange, expanding globally.
Freshworks – First Indian SaaS IPO on NASDAQ.
Razorpay & Groww – Leading fintech platforms transforming payments & investments.
USA:
OpenAI – Pioneering global AI revolution.
Tesla – Redefined the EV industry.
Airbnb – Changed global travel forever.
Both nations produce startups that impact the world — India focuses on scale and affordability, while the US focuses on innovation and global reach.
Risk vs Reward
| Country | Risk Level | Reward Potential | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | Medium | High (long-term) | Sustainable growth with scalability |
| USA | High | Very High | Global disruption, high |
Final Insights
Indian Startups succeed through scale, affordability, and local innovation, but must overcome profitability challenges and funding dependency.
US Startups dominate global markets with innovation, capital, and technology, but face high operational costs and tough competition.
Summary:
- 🇮🇳 India = Growth through Volume & Value.
- 🇺🇸 USA = Growth through Innovation & Capital.
Together, they represent two models of entrepreneurship — one built for the masses, the other built for the world.
